Using 3D Viewers
We are continually working on tuning the 3D viewers for better performance. Keep in mind that interactive 3D rendering can require memory and CPU resources on the browser, and that performance on underpowered computers or bad network connections might be less then optimal
The FaceBase 2 Data Browser includes interactive 3D viewing when datasets include 3D images.
Note that 3D viewing requires WebGL. It’s enabled by default on the latest versions of browsers, but requires a certain amount of memory and bandwidth. See this page for more information if you’re having issues viewing the images.
Here is a video demonstrating the 3D viewer:
You can find detailed description below from a dataset that includes some 3D images:
First, scroll down to and expand the Preview section.
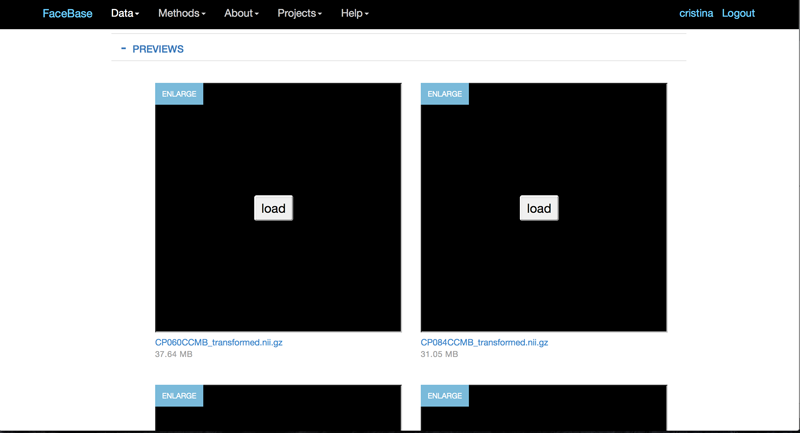
Then click load to load the smaller viewer into the page.

Use your cursor to move the image in the viewer. Hover over Volume to open more controls.
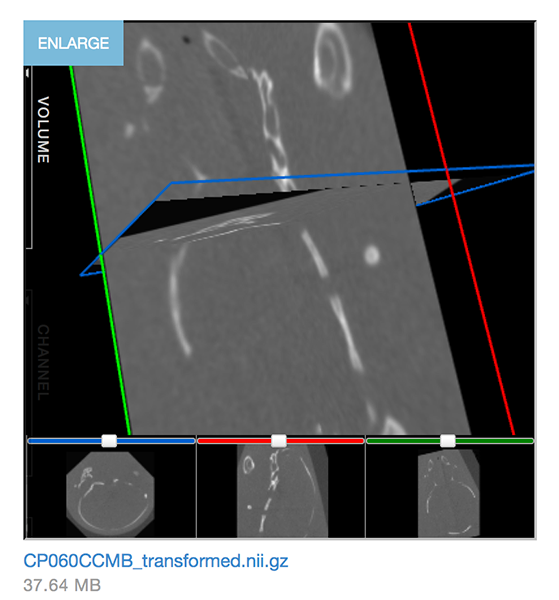
Click the Enlarge link below the preview to open a full-size viewer in a separate browser tab.
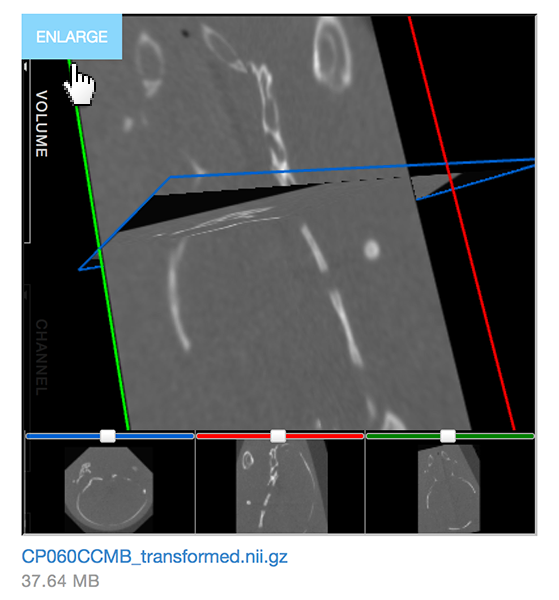
Use keystrokes and the mouse to navigate the 3D viewer
The 3D viewer allows you to use your mouse and keys to manipulate the view:
Note that Internet Explorer 11 only supports the ability of using the mouse wheel to zoom in and out.
Using your mouse:
-
LEFT CLICK + MOVE: Rotate the scene or Window/Level adjustment in 2D
-
SHIFT + LEFT CLICK or MIDDLE CLICK: Pan the scene
-
MOUSE WHEEL UP: Zoom In, fast
-
MOUSE WHEEL DOWN: Zoom Out, fast
-
RIGHT CLICK + MOVE UP: Zoom In, fine
-
RIGHT CLICK + MOVE DOWN: Zoom Out, fine
Using your keyboard:
-
ARROW KEYS: Rotate the scene
-
SHIFT + ARROW KEYS: Pan the scene
-
ALT + UP: Zoom In, fast
-
ALT + DOWN: Zoom Out, fast
-
ALT + LEFT: Zoom In, fine
-
ALT + RIGHT: Zoom Out, fine
-
r: Reset the view to default based on bounding box of all visible objects or a manual configured camera position
Tools and Tips
Here are some tools and tips:
-
Make sure WebGL is enabled or use a WebGL-compatible browser (see below).
-
This site requires Javascript. Go to this URL to make sure javascript is enabled in your browser: http://enable-javascript.com and if it isn’t, follow the instructions for enabling it in your browser.
-
Test your network bandwidth this tool: http://www.speedtest.net
-
Learn how to use your mouse and keyboard to manipulate the 3D viewer.
Enable WebGL
Make sure WebGL is enabled for your browser. WebGL (Web Graphics Library) is a JavaScript API for rendering interactive 3D and 2D graphics within any compatible web browser without the use of plug-ins and is supported by recent browsers. However, sometimes you need to configure a particular setting (specifically for Safari) or upgrade your hardware.
-
Use this link to see if it’s enabled: http://www.doesmybrowsersupportwebgl.com/.
-
Refer to this page and make sure you are using a supported browser.
-
Safari: Safari 8+ supports WebGL by default. In Safari 7, WebGL is supported but is disabled by default so do the following to enable it:
-
Open the Safari menu and select Preferences.
-
Click the Advanced tab in the Preferences window.
-
At the bottom of the window, check the Show Develop menu in menu bar checkbox.
-
Open the Develop menu in the menu bar and select Enable WebGL.
-
-
Internet Explorer: WebGL support is available for IE11 and later but is not supported in previous browsers.
-
Firefox: WebGL should be enabled, but Mozilla does blacklist certain graphics cards and drivers. Go to this page to learn how to upgrade your graphics driver.
-
Chrome: WebGL has been fully supported going back as far as version 31.
-
Chrome supports WebGL on these platforms
-
Windows 7/Windows 8 (Windows 7 or later recommended)
-
Mac OS 10.6 or later (10.8 or later recommended)
-
Linux
-
Chrome OS
-
-
WebGL is available in Chrome on most recent graphics cards and drivers. However, in some cases certain features or all of WebGL isn’t available. Click here for supported configurations.
-